Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Arai, Masatoshi*; Andersen, K. H.*; Argyriou, D. N.*; Schweika, W.*; Zanini, L.*; Harjo, S.; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Harada, Masahide
Journal of Neutron Research, 23(4), p.215 - 232, 2021/12
 He spin filter at a pulsed neutron source
He spin filter at a pulsed neutron sourceOkudaira, Takuya; Ueda, Yuki; Hiroi, Kosuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takata, Shinichi; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi*; Takahashi, Shingo*; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 54(2), p.548 - 556, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:33.1(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Neutron polarization analysis (NPA) for small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) experiments using a pulsed neutron source was successfully achieved by applying a  He spin filter as a spin analyzer for the scattered neutrons. The
He spin filter as a spin analyzer for the scattered neutrons. The  He spin filter covers a sufficient solid angle for performing SANS experiments, and the relaxation time of the
He spin filter covers a sufficient solid angle for performing SANS experiments, and the relaxation time of the  He polarization is sufficient for continuous use over a few days, thus reaching the typical duration required for a complete set of SANS experiments. Although accurate evaluation of the incoherent neutron scattering, which is predominantly attributable to hydrogen atoms in samples, is practically difficult using calculations based on the sample elemental composition, the developed NPA approach with consideration of the influence of multiple neutron scattering enabled reliable decomposition of the SANS intensity distribution into the coherent and incoherent scattering components. To date, NPA has not been well established as a standard technique for SANS experiments at pulsed neutron sources. This work is anticipated to greatly contribute to the accurate determination of the coherent neutron scattering component for scatterers in various types of organic sample systems in SANS experiments at J-PARC.
He polarization is sufficient for continuous use over a few days, thus reaching the typical duration required for a complete set of SANS experiments. Although accurate evaluation of the incoherent neutron scattering, which is predominantly attributable to hydrogen atoms in samples, is practically difficult using calculations based on the sample elemental composition, the developed NPA approach with consideration of the influence of multiple neutron scattering enabled reliable decomposition of the SANS intensity distribution into the coherent and incoherent scattering components. To date, NPA has not been well established as a standard technique for SANS experiments at pulsed neutron sources. This work is anticipated to greatly contribute to the accurate determination of the coherent neutron scattering component for scatterers in various types of organic sample systems in SANS experiments at J-PARC.
Higuchi, Yuki*; Setoyama, Daigo*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Nagai, Yasutaka*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 23(2), p.1062 - 1071, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:52.59(Chemistry, Physical)This study is the first report on liquid water and ice imaging conducted at a pulsed spallation neutron source facility. Neutron imaging can be utilised to visualise the water distribution inside polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs). Particularly, energy-resolved neutron imaging is a methodology capable of distinguishing between liquid water and ice, and is effective for investigating ice formation in PEFCs operating in a subfreezing environment. The distinction principle is based on the fact that the cross sections of liquid water and ice differ from each other at low neutron energies. In order to quantitatively observe transient freezing and thawing phenomena in a multiphase mixture (gas/liquid/solid) within real PEFCs with high spatial resolution, a pulsed neutron beam with both high intensity and wide energy range is most appropriate. In the validation study of the present work, we used water sealed in narrow capillary tubes to simulate the flow channels of a PEFC, and a pulsed neutron beam was applied to distinguish ice, liquid water and super-cooled water, and to clarify freezing and thawing phenomena of the water within the capillary tubes. Moreover, we have enabled the observation of liquid water/ice distributions in a large field of view (300 mm  300 mm) by manufacturing a sub-zero environment chamber that can be cooled down to -30
300 mm) by manufacturing a sub-zero environment chamber that can be cooled down to -30 C, as a step towards
C, as a step towards  visualisation of full-size fuel cells.
visualisation of full-size fuel cells.
 C decoupler with burn-up reduction aiming at 1-MW pulsed neutron source
C decoupler with burn-up reduction aiming at 1-MW pulsed neutron sourceOi, Motoki; Teshigawara, Makoto; Harada, Masahide; Ikeda, Yujiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(7), p.573 - 579, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In pulsed neutron sources, a neutron absorber called decoupler is attached to the moderator to sharpen the neutron pulses for achieving good neutron energy resolutions. Cadmium and boron carbide (B C) are widely used as the decoupler materials. However, it is difficult to use B
C) are widely used as the decoupler materials. However, it is difficult to use B C in MW-class spallation neutron sources owing to high burn-up, which decreases cut-off energy and increase of helium gas swelling. To solve these issues, we introduce the concept of pre-decoupler to reduce neutron absorption in the B
C in MW-class spallation neutron sources owing to high burn-up, which decreases cut-off energy and increase of helium gas swelling. To solve these issues, we introduce the concept of pre-decoupler to reduce neutron absorption in the B C decoupler, which is sandwiched by appropriate neutron absorption materials. Then, we study impacts of the pre-decouplers on B
C decoupler, which is sandwiched by appropriate neutron absorption materials. Then, we study impacts of the pre-decouplers on B C decoupler in terms of burn-up by performing simplified model calculations. It is shown that neutron absorption in B
C decoupler in terms of burn-up by performing simplified model calculations. It is shown that neutron absorption in B C is reduced by 60% by using a Cd pre-decoupler without neutron intensity penalty. Moreover, helium gas swelling in B
C is reduced by 60% by using a Cd pre-decoupler without neutron intensity penalty. Moreover, helium gas swelling in B C is restrained to be one-third of the value when not using the pre-decoupler.
C is restrained to be one-third of the value when not using the pre-decoupler.
 -ray analysis
-ray analysisHuang, M.; Toh, Yosuke; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji
Journal of Applied Physics, 121(10), p.104901_1 - 104901_7, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.9(Physics, Applied)Seya, Michio; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Kureta, Masatoshi
Dai-37-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/02
Large size freight cargo containers are the most volunurable items from nuclear security points of view because of their large volume and weight of cargo inside for hiding heavily shielded objects. For strengthning nuclear security, secure detection of NMs in heavily shielded objects, and safe handling (dismatlement) of detected / suspicious objects for taking out of NMs, are essential. These require the following things, (1) Introduction of secure detection system of NMs, (2) Inspection of deteiled and interior structures of detected objects, (3) Rough chracterization of NMs (for nuclear bomb or RDD etc.) / Confirmation of existence of explosives etc.. By using information obtained by interior inspections, safe dismantlement of objects and taking NMs out are possible. In this papaer, we propose a combined system of X-ray scanning system with NRF-based NDD system using monochromatic  -ray beam not only as a secure detection system of NMs but also interior inspection system (covering (1) and (2)). Also we propose active neutron NDA system using a D-T source for interior inspection of NM part (covering (3)).
-ray beam not only as a secure detection system of NMs but also interior inspection system (covering (1) and (2)). Also we propose active neutron NDA system using a D-T source for interior inspection of NM part (covering (3)).
Yamada, Norifumi*; Takeda, Masayasu; Yamazaki, Dai
Hamon, 24(4), p.288 - 295, 2014/11
no abstracts in English
Futakawa, Masatoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 47(8), p.530 - 535, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Endo, Yasuo
Kotai Butsuri, 40(4), p.239 - 250, 2005/04
no abstracts in English
Kohara, Shinji*; Oishi, Yasuo*; Takata, Masaki*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Suzuya, Kentaro
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 47(2), p.123 - 129, 2005/04
The use of high-energy (E  50 keV) X-rays from SPring-8 allows us to perform X-ray diffraction experiments on disordered materials with the following advantages: high resolution in real space due to the wide range of scattering vector, small correction terms (particularly the absorption correction), and fast diffraction measurement with small amount of samples. Recently, high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed neutron source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than has hitherto been available. Furthermore, the use of reverse Monte Carlo modelling and PDF (pair distribution function) simulation based on high-energy X-ray diffraction data have succeeded in illustrating 3-dimensional structure of disordered materials and disorder in crystalline materials.
50 keV) X-rays from SPring-8 allows us to perform X-ray diffraction experiments on disordered materials with the following advantages: high resolution in real space due to the wide range of scattering vector, small correction terms (particularly the absorption correction), and fast diffraction measurement with small amount of samples. Recently, high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed neutron source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than has hitherto been available. Furthermore, the use of reverse Monte Carlo modelling and PDF (pair distribution function) simulation based on high-energy X-ray diffraction data have succeeded in illustrating 3-dimensional structure of disordered materials and disorder in crystalline materials.
Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Takeuchi, Ken*
Nihon Maikurogurabiti Oyo Gakkai-Shi, 22(2), p.100 - 104, 2005/04
Forsterite Mg SiO
SiO exhibits an orthorhombic structure consisted of two kinds of MgO
exhibits an orthorhombic structure consisted of two kinds of MgO octahedra. Given only 33.3 mol% of SiO
octahedra. Given only 33.3 mol% of SiO in the material, the SiO
in the material, the SiO tetrahedra are isolated within the framework, sharing the O-O bonds with the common edges of the MgO
tetrahedra are isolated within the framework, sharing the O-O bonds with the common edges of the MgO octahedra. If forsterite can be vitrified, an interesting question concerning the glass structure arises because there is insufficient glass forming SiO
octahedra. If forsterite can be vitrified, an interesting question concerning the glass structure arises because there is insufficient glass forming SiO to establish the corner-sharing SiO
to establish the corner-sharing SiO tetrahedral network needed in conventional silicate glasses. A bulk Mg
tetrahedral network needed in conventional silicate glasses. A bulk Mg SiO
SiO glass was synthesized using an aero-acoustic levitation technique and to determine the short- to intermediate-range structure by a combined high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction and reverse Monte Carlo computer simulation. Interestingly, we found that the role of network former is largely taken on by corner- and edge-sharing ionic magnesium species that adopt 4-, 5- and 6-coordination with oxygen.
glass was synthesized using an aero-acoustic levitation technique and to determine the short- to intermediate-range structure by a combined high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction and reverse Monte Carlo computer simulation. Interestingly, we found that the role of network former is largely taken on by corner- and edge-sharing ionic magnesium species that adopt 4-, 5- and 6-coordination with oxygen.
 Sb
Sb Te
Te
Shamoto, Shinichi; Yamada, Noboru*; Matsunaga, Toshiyuki*; Proffen, T.*; Richardson, J. W.*; Chung, J.-H.*; Egami, Takeshi*
Applied Physics Letters, 86(8), p.081904_1 - 081904_3, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:81.94(Physics, Applied)Local structure of NaCl-type crystalline Ge Sb
Sb Te
Te has been studied by the atomic pair distribution function analysis of pulsed neutron powder diffraction data. We have found the large displacement of germanium atoms in this crystalline phase. Usually, such a large lattice distortion has disadvantage for the electric conductivity. The electronic band structure, however, implies that this significant distortion in addition to the lattice defect at Na site reduces only thermal conductivity, while the highly ordered tellurium atoms at Cl site keep high electric conductivity.
has been studied by the atomic pair distribution function analysis of pulsed neutron powder diffraction data. We have found the large displacement of germanium atoms in this crystalline phase. Usually, such a large lattice distortion has disadvantage for the electric conductivity. The electronic band structure, however, implies that this significant distortion in addition to the lattice defect at Na site reduces only thermal conductivity, while the highly ordered tellurium atoms at Cl site keep high electric conductivity.
 studied by neutron diffraction
studied by neutron diffractionChung, J.-H.*; Proffen, T.*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Ghorayeb, A. M.*; Croguennec, L.*; Tian, W.*; Sales, B. C.*; Jin, R.*; Mandrus, D.*; Egami, Takeshi*
Physical Review B, 71(6), p.064410_1 - 064410_11, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:77 Percentile:90.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)LiNiO (S=1/2) forms a triangular lattice with the possible magnetic frustration, but the exact state of spin correlation has not yet been known. While there is no signature of long-range Jahn-Teller distortion, local JT distortion has been suspected. We have performed neutron diffraction and atomic pair-density function analyses up to unprecedented large distances to discover a number of unusual features, such as anomalous peak broadening, local JT distortion, sharp oxygen-oxygen distance correlations, and inverted temperature dependence of medium range correlation. These observations are best explained by local orbital ordering of Ni
(S=1/2) forms a triangular lattice with the possible magnetic frustration, but the exact state of spin correlation has not yet been known. While there is no signature of long-range Jahn-Teller distortion, local JT distortion has been suspected. We have performed neutron diffraction and atomic pair-density function analyses up to unprecedented large distances to discover a number of unusual features, such as anomalous peak broadening, local JT distortion, sharp oxygen-oxygen distance correlations, and inverted temperature dependence of medium range correlation. These observations are best explained by local orbital ordering of Ni ions into three sublattices. This orbital ordering, however, cannot develop into long-range order because of the strain field it generates, and domains of about 10 nm in size are formed. Domains are susceptible to random pinning by impurities ssite disorderd resulting in the loss of structural long-range order. We suggest that this local orbital ordering is the basis for the complex magnetic properties observed in this compound.
ions into three sublattices. This orbital ordering, however, cannot develop into long-range order because of the strain field it generates, and domains of about 10 nm in size are formed. Domains are susceptible to random pinning by impurities ssite disorderd resulting in the loss of structural long-range order. We suggest that this local orbital ordering is the basis for the complex magnetic properties observed in this compound.
Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*
Hamon, 15(1), p.51 - 54, 2005/01
Neutron spin handling could be used for beam control and spectroscopy. Energy analysis could be performed with Drabkin energy filters, by which inelastic component with a 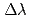 , a
, a 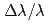 or a
or a 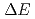 could be extracted for all incident wavelength. Pulsed spin-flipper and polarization analyzer could be used as a neutron chopper (spin-flip chopper) whose opening time, number of windows and phase are controlled independently. It was demonstrated that S/N ratio can be enhanced up to 1.5
could be extracted for all incident wavelength. Pulsed spin-flipper and polarization analyzer could be used as a neutron chopper (spin-flip chopper) whose opening time, number of windows and phase are controlled independently. It was demonstrated that S/N ratio can be enhanced up to 1.5  10
10 by installing three spin-flip choppers in sequence.
by installing three spin-flip choppers in sequence.
Katagiri, Masaki
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 529(1-3), p.254 - 259, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.72(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Yujiro
Proceedings of ICANS-XVI, Volume 1, p.13 - 24, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Noboru; Harada, Masahide; Kai, Tetsuya; Teshigawara, Makoto; Ikeda, Yujiro
Journal of Neutron Research, 11(1-2), p.13 - 23, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Noboru
Reports on Progress in Physics, 66(3), p.339 - 381, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:64.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Suzuya, Kentaro
Hamon, 13(1), p.51 - 55, 2003/01
With the arrival of the latest generation of synchrotron sources and the introduction of advanced insertion devices, the high-energy (E  30 keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. Recently, the high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available. We have developed a two-axis diffractometer for glass, liquid and amorphous materials at the SPring-8 high-energy X-ray diffraction beamline BL04B2. Furthermore, we have succeeded to analyze the intermediate-range order of network forming glasses, SiO
30 keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. Recently, the high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available. We have developed a two-axis diffractometer for glass, liquid and amorphous materials at the SPring-8 high-energy X-ray diffraction beamline BL04B2. Furthermore, we have succeeded to analyze the intermediate-range order of network forming glasses, SiO , B
, B O
O , and GeO
, and GeO by the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique with special focused on the ring structures using both high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data.
by the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique with special focused on the ring structures using both high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data.
Oyama, Kenji*; Ito, Shinichi*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Suzuki, Junichi; Matsuda, Masaaki; Kuwahara, Keitaro*; Arai, Masatoshi*
Applied Physics A, 74(Suppl.1), p.S1598 - S1600, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English